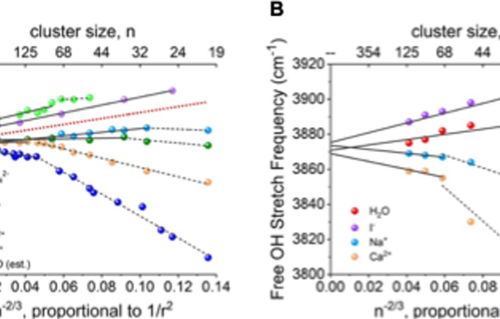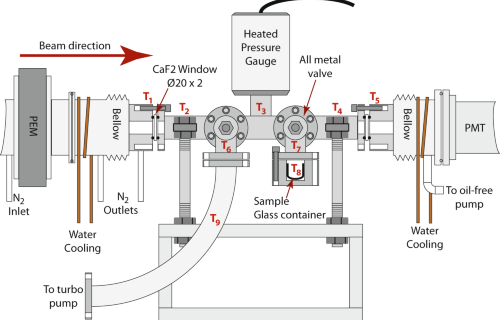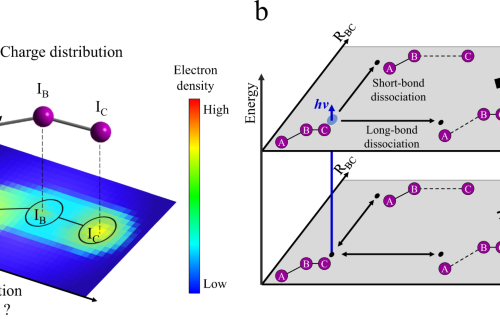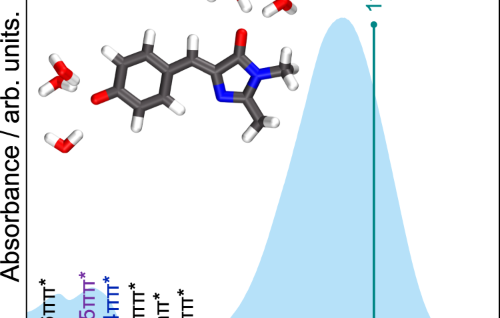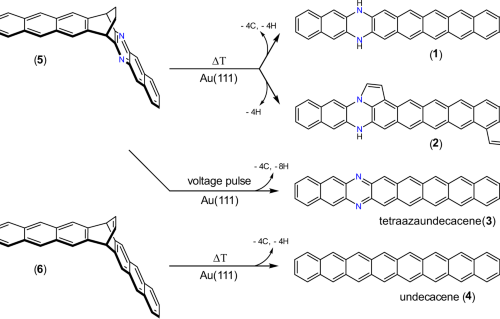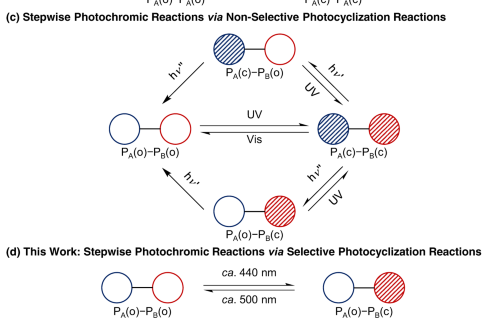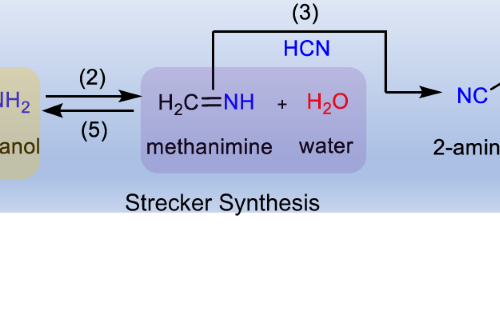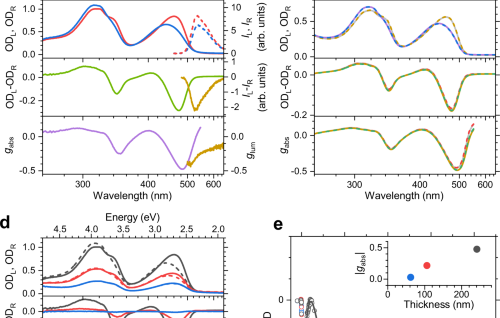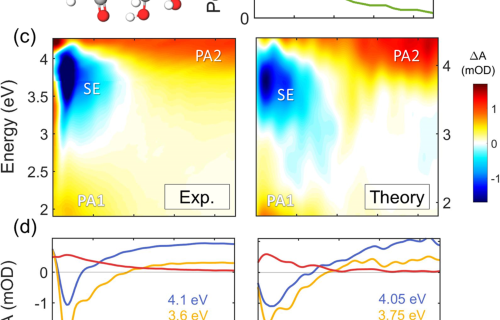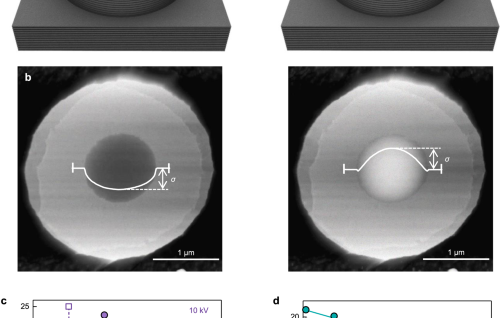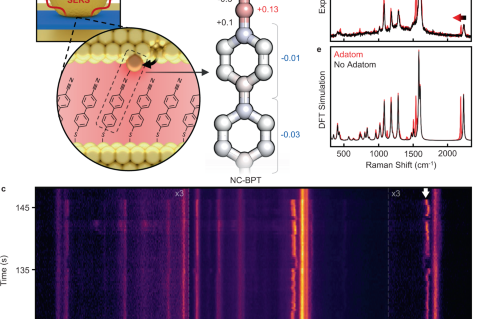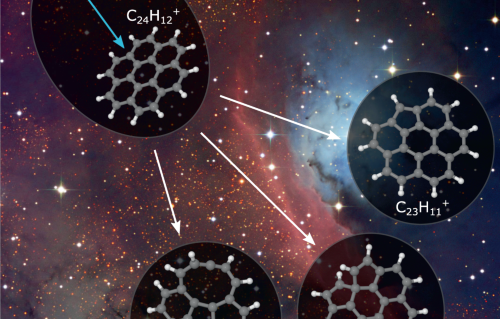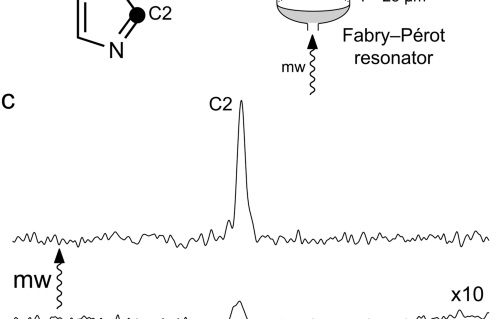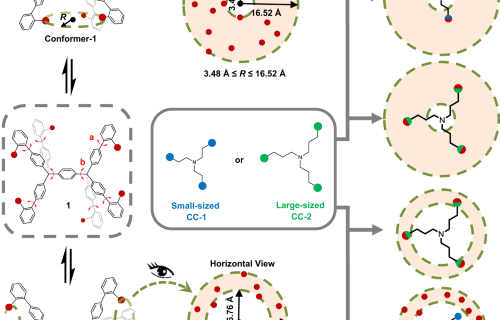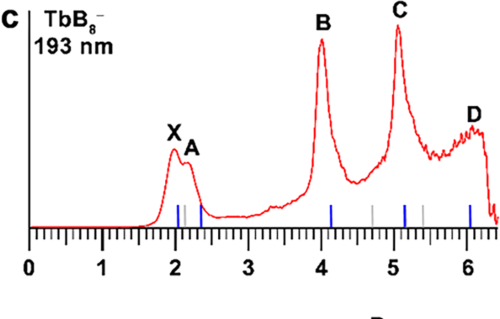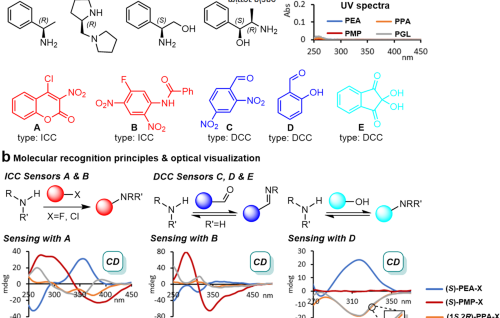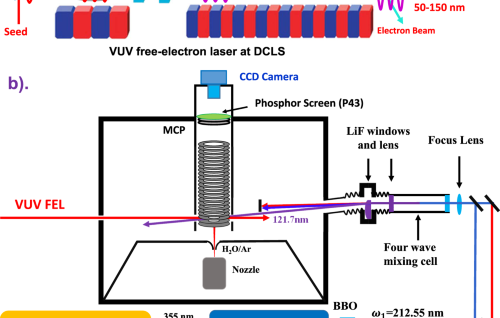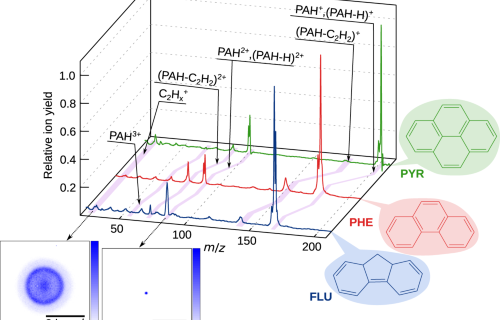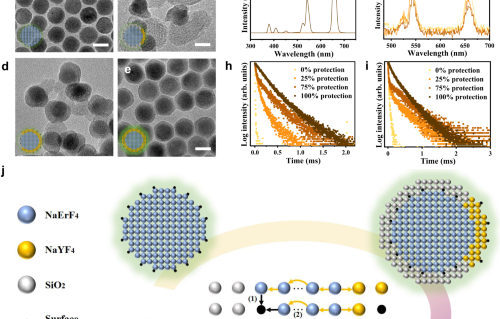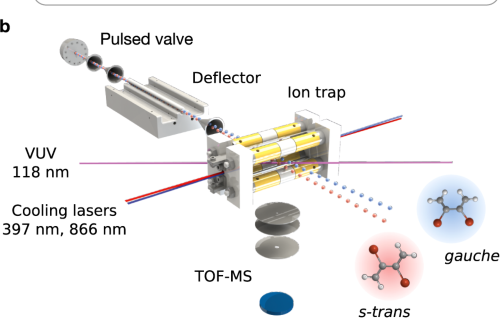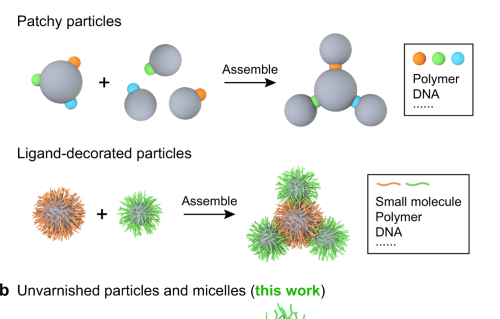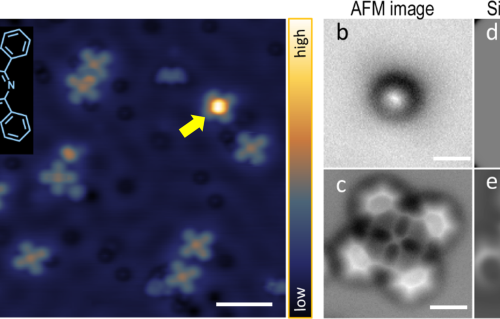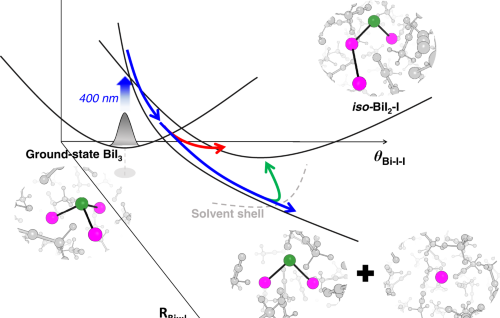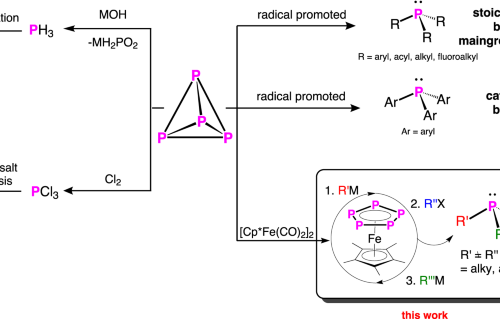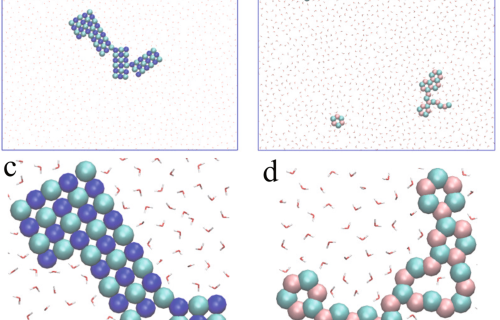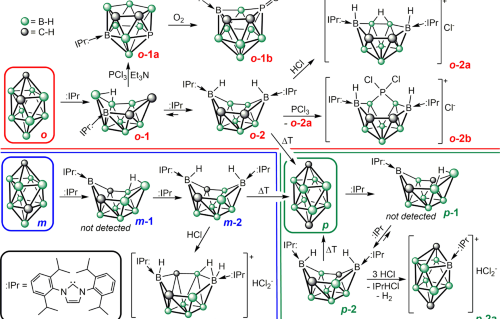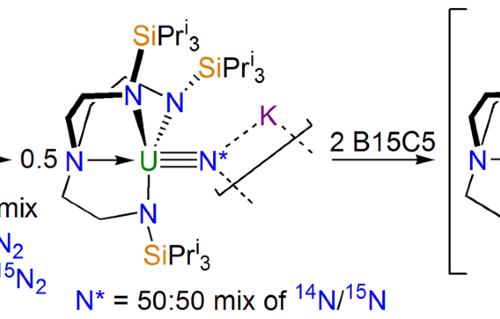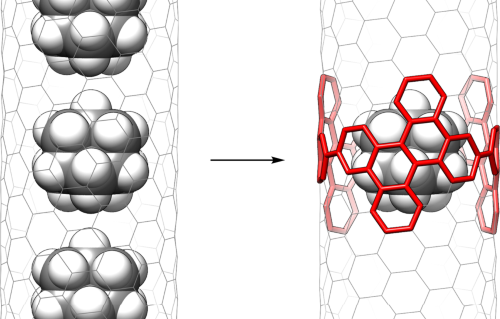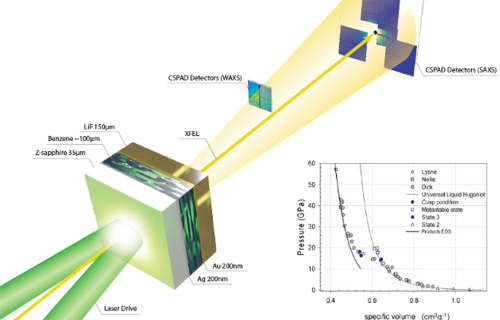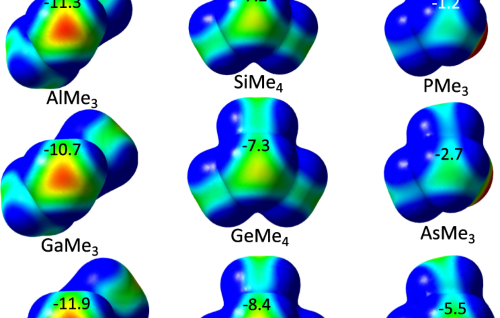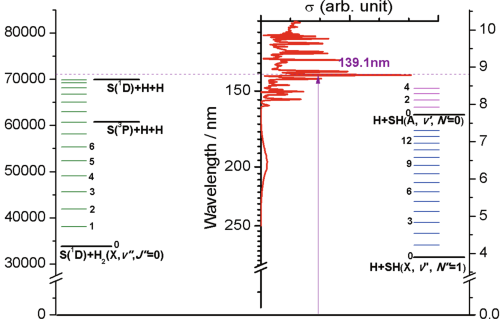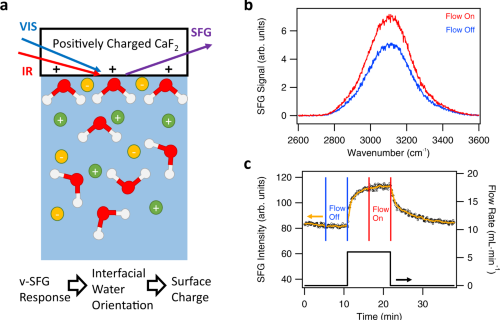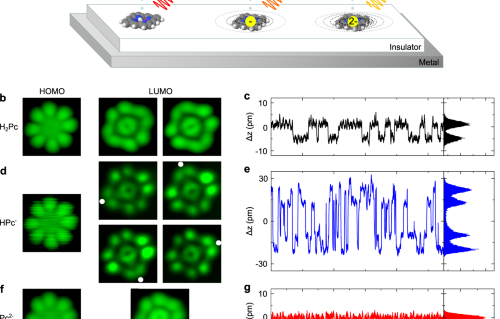
Internal Stark effect of single-molecule fluorescence

Focus |
From atoms and molecules, to supramolecular and nanoscale assemblies; from the gas phase to liquids and crystals, and matter under extreme conditions: this page highlights some of the most exciting works in physical chemistry and inorganic chemistry, aiming to explain…