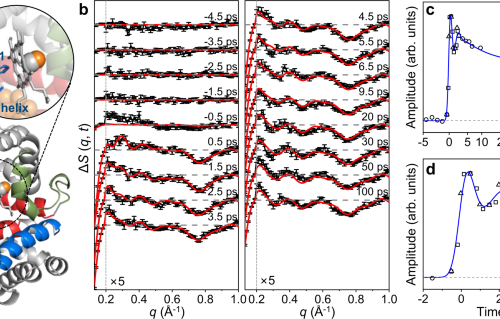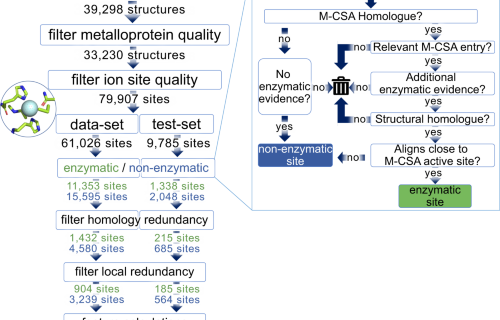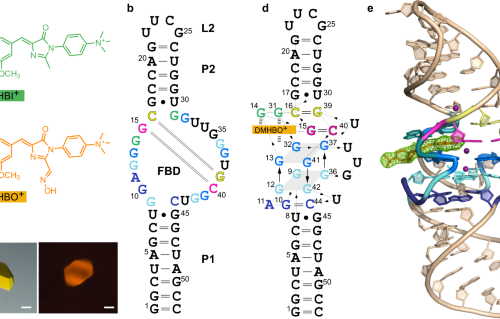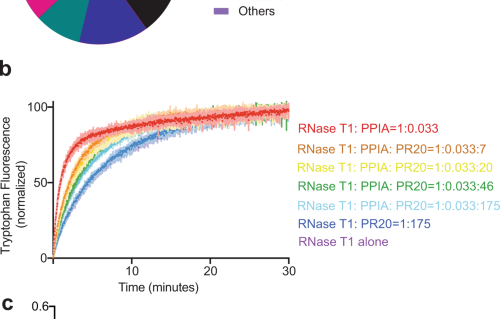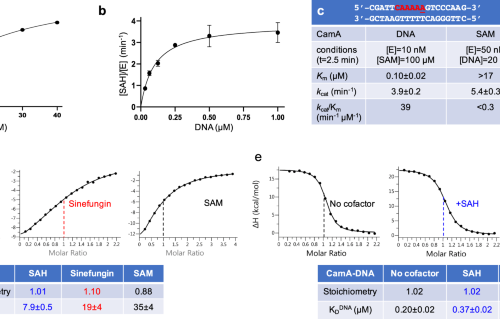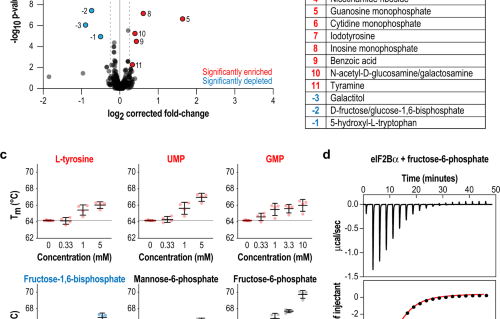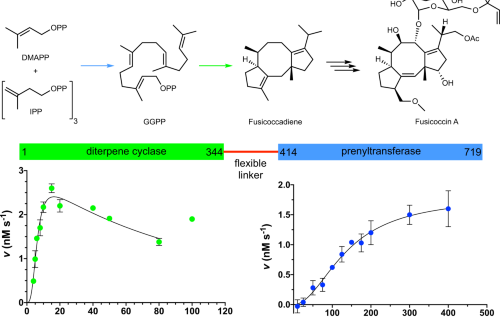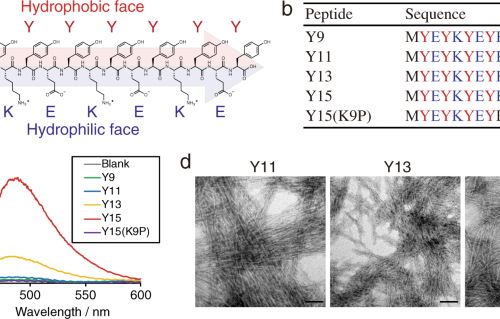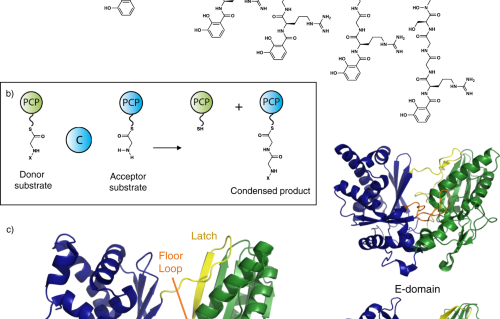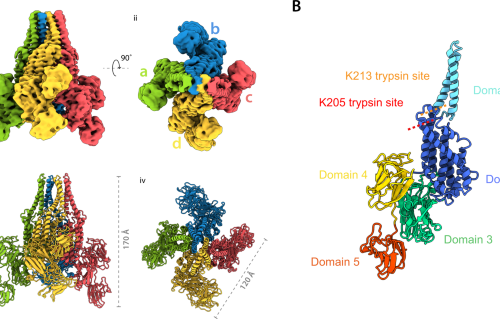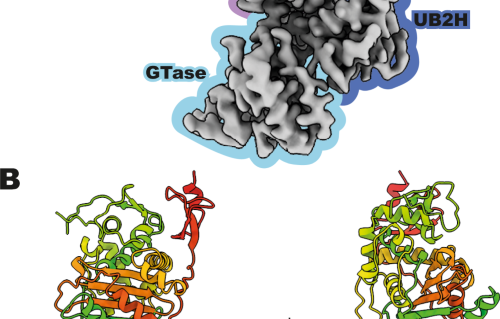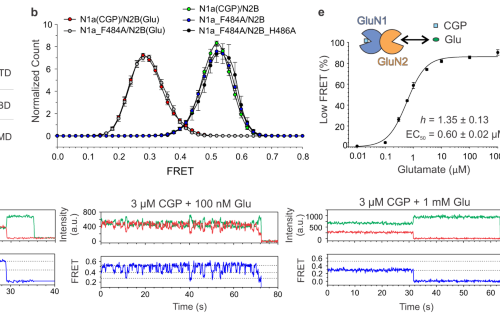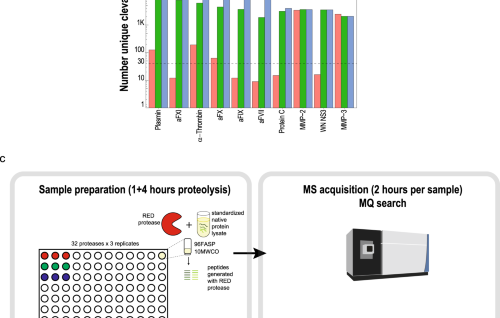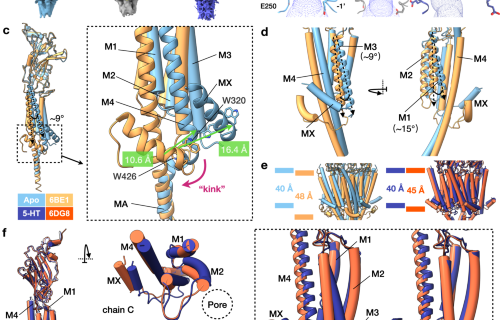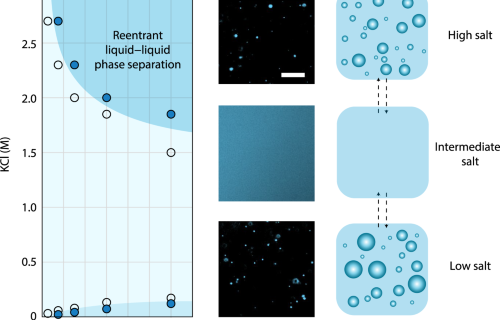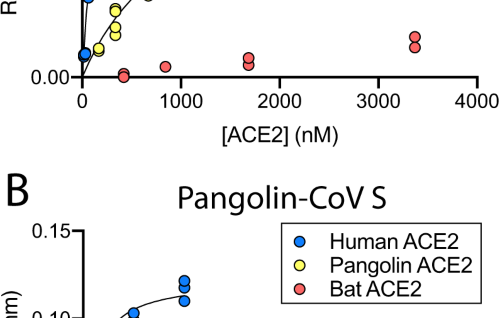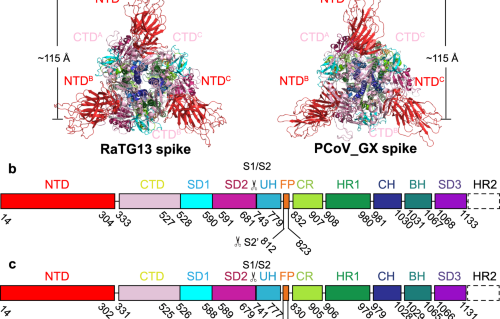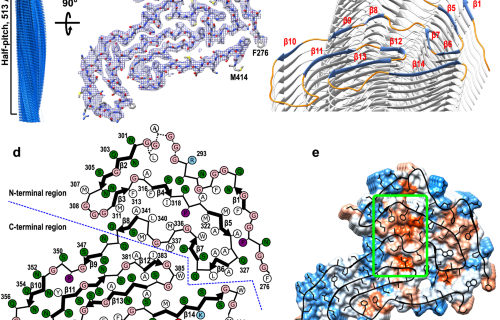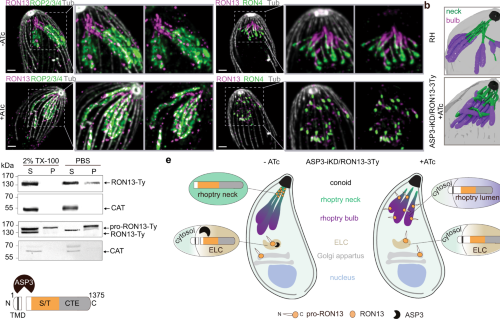
Structural insights into an atypical secretory pathway kinase crucial for Toxoplasma gondii invasion